Growth abnormalities
Reasons growth abnormalities.
In the table given below, we placed photos and pointed out cultivation problems that a mushroom grower might come across in his practice. We tried to point out the reasons these problems might occur. Perhaps, using our table, someone will be able to determine the reason for the occurrence of mushroom growth abnormalities and eliminate them.
Areas of compost not grown with mycelium or poor mycelium growth in the compost. | ||
| • Pythium disease (black compost); • The presence of nematodes or fly larvae; • Improperly prepared compost; • Ammonia remains in the compost; • Excessive compost humidity; • Degenerating strain; • Low-quality, diseased and nonviable mycelium; • Overly high compost temperature (above 30°C) on spawn growth stage. | ||
Poor and uneven mycelial growth in the casing layer. | ||
| • overly high or low temperature of the mixture; • incorrect pH level of the mixture; • unsuitable mixture components; • poor mixing of casing soil ingredients; • overly humid or overly dry casing layer; • nonuniform casing soil application (different height); • casing layer that is too thick (above 6 cm); • poor mycelial growth; • the infection of compost by competing fungi and the presence of pests, such as nematodes. | ||
The formation of stroma | ||
| • low-quality degenerating strain; • mycelial growth in a poorly ventilated casing layer, with a high concentration of carbon dioxide, high temperature and humidity and a high volume of evaporation; • overly long period of mycelial growth in the casing layer. The problem can be solved by regulating the ventilation system, lowering the carbon dioxide concentration and the air temperature; and slight loosening of the casing layer; in serious cases, casing layer might be applied again. | ||
Mycelial growth in the casing layer and its subsequent disappearance. | ||
| • virus disease; • nematodes; • overly high pH level; • improper casing mixture preparation; • improper watering of the casing layer. | ||
Pins do not form. | ||
| • imbalanced pH level; • casing layer that is overly humid or overly dry; • an excess content of magnesium in lime; • high level CO2; • improper pinning technique; • degenerating strain; • the presence of nematodes; • virus disease. | ||
The appearance of early mushrooms (before or at pinning). | ||
| • a thin casing layer along the edges of the beds; • nonobservance of the climatic regime on the stage of mycelial growth in the compost, that is, early entry of fresh air and the decrease of CO2 concentration; • low temperature. | ||
Poor or insufficient pinning. | ||
| • nonobservance of the pinning regime for a specified strain (of poor pin formation); • low air humidity; • excessively high concentration of CO2; • excessively high air temperature; • casing surfaces damaged with a strong water head at watering; • improper casing layer structure. | ||
Uneven pinning. | ||
| • nonuniform casing layer (different height); • nonuniform watering of the casing layer; • casing layer damages caused by a strong water head; • nonuniform distribution of air in the growing room and as a result of different microclimate conditions. | ||
Excessive (abundant) pinning. | ||
| • inappropriate pinning regime for easily-pinning strain; • abrupt pinning regime, that is, a sudden decrease in compost and air temperature; • thin casing layer. | ||
Dying pins. | ||
| • strain extinction; • excessively high level of humidity; • excessively high temperature; • a lack of fresh air, and a high level of CO2; • insufficient nutrition; • insufficient amount of moisture in the casing layer; • untimely irrigation (too early); • inappropriate climate conditions after irrigation (the formation of condensate on mushrooms); • virus disease; • severe pest infestation (flies, nematodes) or diseases. | ||
The formation of pins inside the casing layer and dirty mushrooms. | ||
| • mistakes during the pinning process (untimely pinning); • a very dry casing surface; • the casing soil composition due to which pieces of peat remain on mushroom caps; • improper harvesting technique. | ||
The formation and mushroom growth in clusters. | ||
| • tendency of the strains to form clusters; • low periodical air temperatures during pinning. | ||
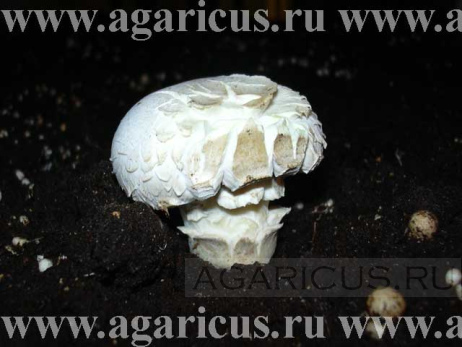
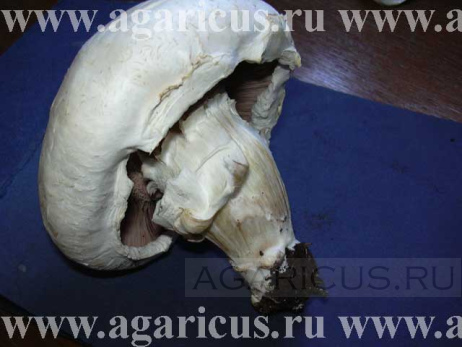
The deformation of fruit bodies, misshapen mushrooms, mushroom intergrowth. | ||
| • low-quality, degenerating strain; • excessive level CO2, imbalanced climatic conditions; • Mycogone or Verticillium diseases; • The effect of a great amount of pesticides and other chemicals. | ||
The formation of scales or «crocodile skin». | ||
| • very dry air; • strong air movement with low relative humidity; • shortcomings in the air supply and distribution system; • tendency of the strain to form scales; • damage done by pesticides. | ||
Outgrowths on mushroom caps – «cock’s comb». | ||
| • an overdose of pesticides; • casing layer infected with chemicals; • the effect of exhaust and harmful gases, heating appliances, diesel oil, formalin vapors, dissolvers, paint. | ||
Tough gills and open veil. | ||
| • the susceptibility of some strains; • disruptions of climate conditions. | ||
Thick stipes, small caps. | ||
| • excessively high CO2 level on the initial stage of growth. | ||
Long stipes. | ||
| • the growth of a big amount of mushrooms due to excessive pin formation, accumulation of a great amount of CO2; • mummy disease; • virus disease. | ||
Hollow and split stipes. | ||
| • improper irrigation; • the application of moist casing layer, its drying, and quickly bringing it to the required humidity level. | ||
A small cap on a normal stipe. | ||
| • improper climatic conditions for specific strains; • the susceptibility of some strains. | ||
Watery mushrooms. | ||
| • virus or bacterial disease; • the nearness of areas colonized with trichoderma; • improper irrigation regimes; | ||
A change in color of fruit bodies (darkening). | ||
| • bacterial blotch disease; • phenolic vapors; • improper use of pesticides; • the disruption of climatic conditions after irrigation; • leaking of water from the beds of compost above. | ||



































Lko:
Saheb hamare mushroom dry bable se pura form doob chuka hai ismein Ham Kya Karen Sahab Koi upay Ho to...
Production of Compost, Personal opinion (part 3). Wet...Abimbola Olaniyi-Balogun, Lagos Nigeria:
Hello there, I made mushroom compost using the long composting method. I used wet chicken manure, fresh...
Mushrooms in KazahstanZagreb, Croatia:
My name is Zlatko Vidmar.
Without chicken manure compost? Yes, it's possible...I am in modern mushroom growing over 40 years.
I see your farm and if...
nanyuki:
my email is samuelnjogo@gmail.com
Without chicken manure compost? Yes, it's possible...nanyuki:
i want to learn like a child on compost making for mushroom
Mushrooms in KazahstanVELLORE TAMILNADU INDIA:
SUITABLE JOBS – MUSHROOMS GROWER / COMPOST / SPAWN OR RELAVANT FIELDS
Without chicken manure compost? Yes, it's possible...Dear Hiring Manager...
Patna:
PLEASE SEND YOUR FORMULA without-chicken-manure-compost
watering first flush mushroomswasil, Malaysia:
i suggest you not to water on mush just maintain the good humidity if you not have any auto system for...
Compost Production. Personal opinion (Part 2)NARENDER SEHRAWAT, FARIDABAD NCR:
COMMON PROBLEM IN PHASE 1 BUNKAR IS THE UNBALANCED TEMERATURE, IT STARTS FROM 50-55 DEGREES TO 78-82...
Without chicken manure compost? Yes, it's possible...Hannes, Plettenberg Bay, South Africa:
Can you give me more details on compost without chicken manure for mushroom growing, what alternatives...